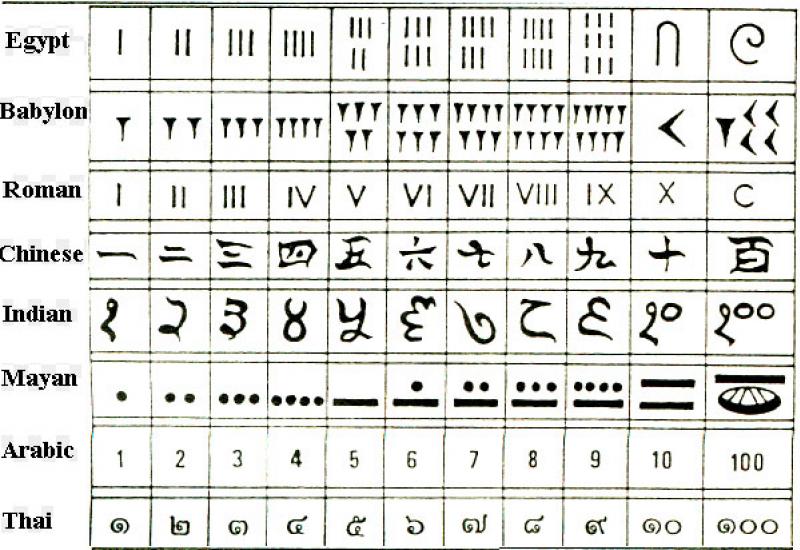
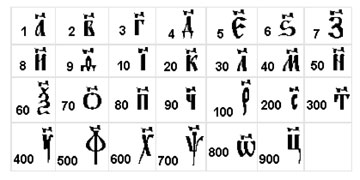
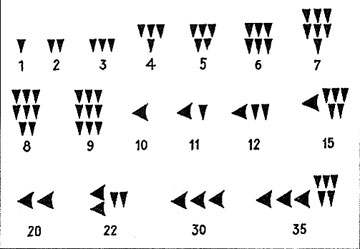
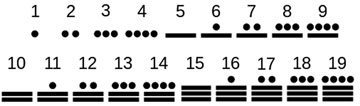
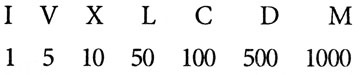A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, and so forth. A notational symbol that represents a number is called a numeral. [wiki].
|
Number ( mathematical) abstract; literal; algorithmic; multiplace; multudigit; polygonal; square-free; biquadretic; eigenvalue; main; alternion; hypertranscendental; end; binary; double figure; two-figure; real; positive; perfect; fraction; Euclidean; іdeal; concrete; surd; quasiperfect; complex; identical; mixed; approximate; redundant; positive; deficient; odd; non-integral; standard; reciprocal; simple quantity; one-figure; оrdinal; even; pentagonal; primary; half-integer; radicand; pyramidal; polygonal; comparative; ordinal; derived; beginning; prime; quasi-random; pseudoprime; pentagonal; rank; rational; rib; bit; regular; fifite; сomposite; spectral; tabular; transfinite; transcendental; three-digit; tree figures; imaginary; figurate; whole. |
Numbers ( mathematical) associative; prime-twins; hyperprimary; complex conjugate. Number (physical) aperture; atomic; pure; isotropy; quantum; coordination; rejection; magic; scaled; transmission; total chromatic; cardinal; wave; chromatic. Number (engineering.) knock value; gear-ratio. Number (astronomical) hourly rate; Zurich. Number (geological) anorthite. |
How numbers were marked: The number of Slavs
Babilonian numbers
Japanese numbers
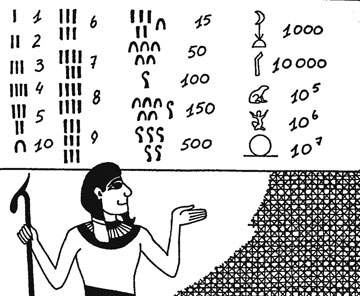
Maya numbers Egyptian numbers Roman numerals |